Knee pain is a common issue among adults of all ages. One of the most common causes of knee pain is osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee pain like osteoarthritis is most commonly associated with general wear and tear from daily activities like standing, walking, and lifting. For many people, knee pain progresses from a nuisance to a debilitating condition. To fully understand why osteoarthritis of the knee occurs, we must first understand the anatomy of the knee.
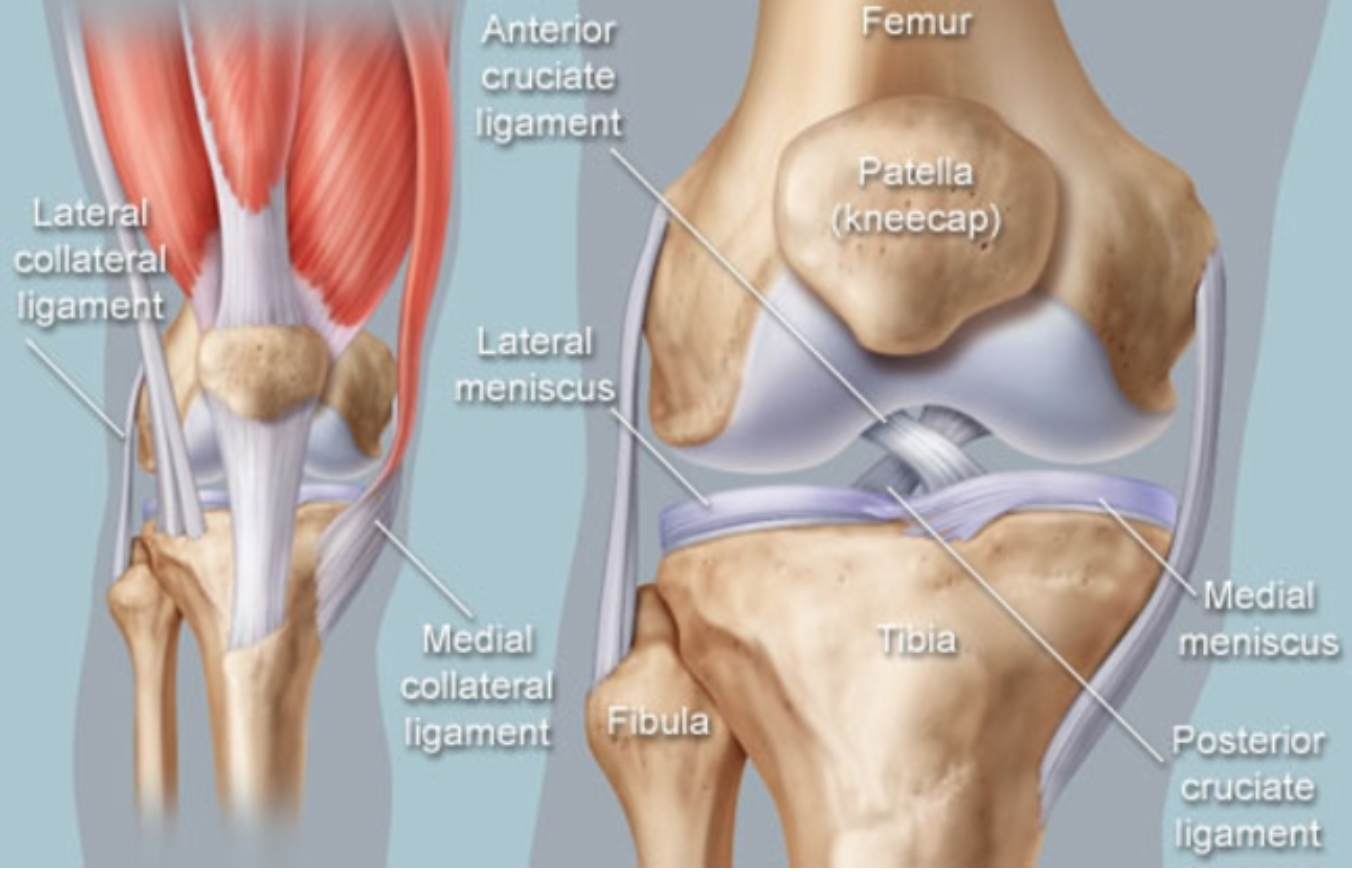
Anatomy of the Knee
The knee bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities such as lifting, kneeling, standing, walking, and jogging. The constant stress that is put on the knee makes it a vulnerable joint. The knee is formed by three bones, the femur (the thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). Each bone is covered with a layer of cartilage that helps to protect the knee by absorbing shock. Synovial fluid is present within the cartilage, this fluid acts as a lubricant to reduce friction between the cartilage and joint. The bones that make up the knee are held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The tendons are tough cords made up of tissue that connect the muscles to the bones. The ligaments are elastic bands that connect bone to bone. Some of these ligaments provide stability and protect the joints. While others prevent too much movement from occurring.
What Causes Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a degenerative process where the cartilage in the knee joint gradually wears away over time. This degeneration may be caused by excess stress on the joints from being overweight or from repetitive stress. When the cartilage wears down, the bones of the joint rub more closely against one another and the shock absorption benefits are diminished leading to progressive damage. As the cartilage wears the lubricant of the synovial joint is also decreased resulting in an increase of friction between the joint. The rubbing of the bones results in stiffness, swelling, decreased motion of the joint, and the formation of painful bone spurs. As the joint space diminishes the ligaments surrounding the joints are no longer taught like they should be and begin to fold in on themselves, this results in instability of the joint and puts osteoarthritis sufferers at greater risk for a knee injury. There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing osteoarthritis including age, weight, heredity, athletics, and metabolic disorders.
Treatment for Arthritis of the Knee
Conventional treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee consists of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid, braces, physical therapy, and when all else fails, surgery. Those suffering from knee pain know the frustrations of failed treatments. For many arthritis sufferers, prescription medication dosages continue to increase as the degeneration continues to get worse. At Abundant Life Health Center, we offer our patients an alternative to medications filled with side effects and invasive and often unsuccessful surgeries. Our comprehensive knee protocol physically increases the joint space within the knee to restore the flow of synovial fluid to the joint and prevent the bones from rubbing together. Restoring the joint space helps to reverse the damage and pain that the bones rubbing together has caused. Our team of doctors works together to identify and address all the factors playing a role in osteoarthritis. If you are suffering from knee pain, contact our office to find out how we can help you.